Periodontal Disease
Periodontal Disease
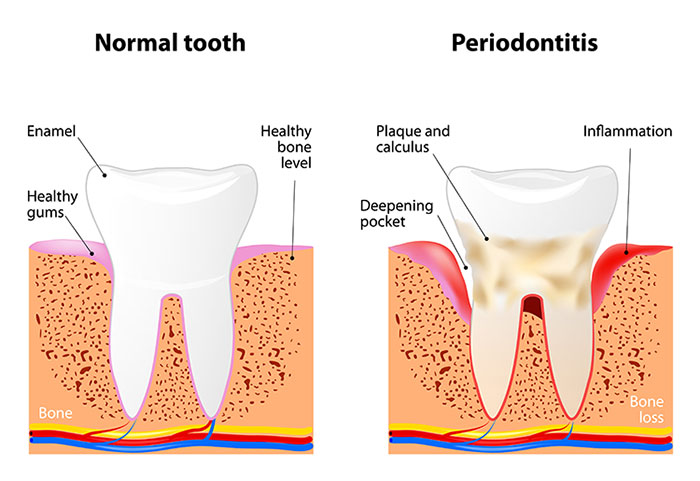
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a bacterial infection in the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. It can be divided into several categories.
The first stage is called “gingivitis” and is characterized by gum tissue that is red, puffy and bleeds easily when touched with a toothbrush, floss or dental instrument.
The second, third and fourth stages are initial, moderate and advanced “periodontal disease,” respectively. These stages are different from gingivitis because the infection has destroyed the bone supporting the teeth, causing eventual tooth loss. The treatment is more involved at these stages, usually consisting of a special cleaning with anesthesia and sometimes gum surgery.
Periodontal-Disease
The American Dental Association says that over 75-80% of all adults have or will have some form of gum disease.
Periodontal disease has a high statistical correlation with chronic debilitating disease, such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease and arthritis. Multiple tooth loss is most commonly caused by periodontal disease, i.e. gum and bone disease.